One of the most important device hardening systems is App Control for Business. With App Control for Business, you can choose which apps can be used on your device. It is possible to prevent any application from running. It is also possible to create exceptions for applications that are approved by the organization to run on the devices and allowing apps installed with Intune.
As of Intune Service Release 2508, the App Control for Business feature is generally available under the Endpoint Security node in Intune. This makes the use of App Control a little bit easier. This blog will show you how to set up App Control.
People often talk about the following options when it comes to App Control:
- Windows Defender Application Control
- AppLocker
- App Control for Business
App Control for Business is the newest addition to Intune. It makes it easier to use Windows Defender Application Control because it has built-in controls and an easy way to upload xml files. WDAC is the core technology, and it’s used in Windows and App Control for Business. App Control for Business is the Intune management interface and the current “brand” name. AppLocker is an older technology that blocks applications. I don’t recommend using AppLocker anymore. Microsoft doesn’t update this technology, and it has fewer security features than App Control.
Configuring App Control for Business in a basic way is done in phases. The phases are:
- Setup the managed installer
- Setup the base policy
- Setup the supplemental policy
Managed Installer
First we need to setup the managed installer.The Managed installer makes sure that apps installed via Intune are allowed by default. Intune applications are managed by the organization, so it is practical to allow these applications. Here’s how to set up the managed installer:
- In the Intune portal, go to Endpoint Security > App Control for business.
- In App Control for Business, go to the Managed Installer tab.
- In Managed Installer, select Create.
- In the wizard, in the basic tab, add a name and description, select Next.
- In the settings tab, set Enable Intune Managed Extension as Managed Installer to Enabled, select Next.
- In the Scope Tags tab, select Next.
- In the Assignments tab, add a group that has devices in it, select Next.
- In the Review tab, select Save.
App Control for Business base policy with built-in controls
The App Control for business built-in controls policy is the base policy for App Control. This policy is a set of basic rules for configuring App Control for Business. The following is defined in a built-in controls policy:
- Policy creation type: The policy is either created using XML or built-in controls.
- Audit mode: To test the result of the App Control policy, you need to set the policy to audit mode. The policy blocks applications when it is not set to audit mode.
- Trust apps from managed installer: Apps from Intune (in this case) will be trusted.
- Trust apps with good reputation: Apps with a good reputation will be trusted. The Microsoft Intelligent Security Graph is used for this. This is mainly used to reduce helpdesk calls and end-user frustration because an app is blocked.
Here’s how to set up the built-in controls policy:
- In the Intune portal, go to Endpoint Security > App Control for business.
- In App Control for Business, go to the Policies tab.
- In Policies, select Create.
- In the wizard, in the basic tab, add a name and description, select Next.
- In the configuration settings tab, set Policy create type to Built-in controls.
- In the configuration settings tab, set Audit mode to Enabled if you want to audit first and set to Disabled if you want to block apps. We will choose disabled to block apps.
- In the configuration settings tab, set Trust apps from managed installer to Enabled if you want to trust Intune managed apps and set to Disabled if you don’t want to trust them. We will choose Enabled to allow Intune Apps.
- In the configuration settings tab, set Trust apps with good reputation to Enabled if you want to trust those apps and set to Disabled if you don’t want to trust them. We will choose Disabled to block all third-party apps.
- Select Next.
- In the Scope Tags tab, select Next.
- In the Assignments tab, add a group that has devices in it, select Next.
- In the Review tab, select Save.
App Control for Business base policy with XML upload
In addition to setting the built-in controls, it is also possible to upload an XML file. We can create this XML file using the App Control Wizard. It is quite easy to create an XML file. I prefer this because we can see what is being set up. Here’s how to create the XML file:
- Download and run the App Control Wizard (Microsoft App Control Wizard).
- In the wizard, select Policy Creator.
- Select a Policy type, we will select Multiple Policy Format (we want to set up a supplemental policy later) and select Base Policy, select Next.
- Now we can choose different Base Templates:
- Default Windows Mode:
- Most restrictive, allow core Windows components
- Allow Microsoft Mode:
- Allow core Windows components plus any software signed by Microsoft
- Signed and Reputable Mode:
- Allow core Windows components plus any software signed by Microsoft plus everything trusted by the ISG (Authorize reputable apps with the Intelligent Security Graph (ISG) | Microsoft Learn)
- Default Windows Mode:
- Select the Allow Microsoft Mode (blocking all third-party apps). Specify a name and location for the XML file, select Next.
- Select Managed Installer (allowing apps from Intune) and deselect Audit Mode (to set up block mode), select Next.
- Select Next and the policy is created.
We need to set up the base policy with the XML file in Intune:
- In the Intune portal, go to Endpoint Security > App Control for business.
- In App Control for Business, go to the Policies tab.
- In Policies, select Create.
- In the wizard, in the basic tab, add a name and description, select Next.
- In the configuration settings tab, set Policy create type to XML upload (Default).
- In the configuration settings tab, set XML upload to browse for the created XML file.
- Select Next.
- In the Scope Tags tab, select Next.
- In the Assignments tab, add a group that has devices in it, select Next.
- In the Review tab, select Save.
App Control for Business supplemental policy
We have created a base policy that defines what is allowed and what is not allowed. As I said before, we define things like Windows core components, software signed by Windows, and apps that are trusted by ISG. We need to create a supplemental policy to allow third-party apps. The base policy and supplemental policies work together. You can install multiple supplemental policies on a device, but only one base policy. This blog won’t cover setting up an App Control for Business supplemental policy. I’ll talk more about that in a future blog post.
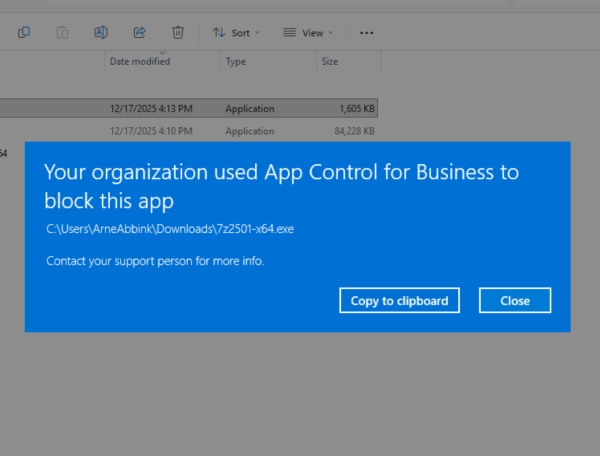
The result
These steps will result in the implementation of an App Control for Business policy. This policy will block all third-party apps and will only allow Core Windows Components and software signed by Windows. The image below shows that 7zip will be blocked when installing: